
Introduction
Andrographis paniculata has been extensively used in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine due to its potent bioactive compounds. The plant is particularly renowned for its immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Extracts derived from the plant are utilized in various herbal formulations, dietary supplements, and pharmaceutical preparations.
Botanical Characteristics
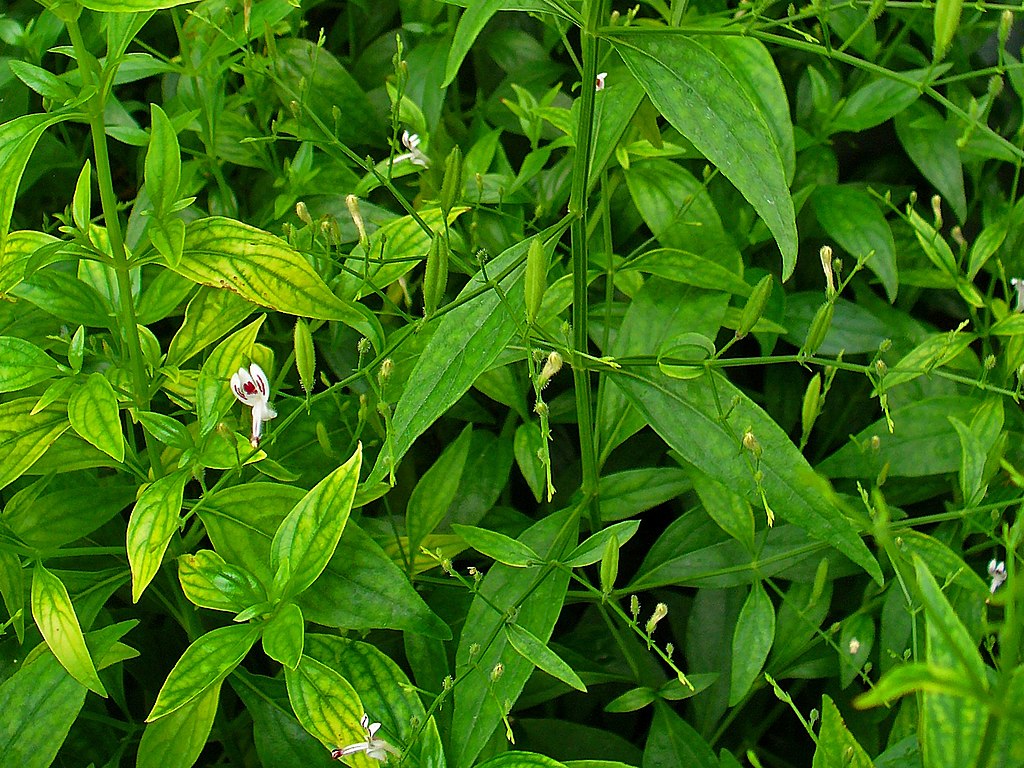
Andrographis paniculata, commonly known as Green Chiretta or King of Bitters, is a herbaceous plant belonging to the Acanthaceae family. It is a well-known medicinal plant widely distributed across tropical and subtropical regions of South Asia, including India, China, and Thailand. This perennial herb has gained significant attention for its therapeutic properties and is widely cultivated for medicinal purposes.
Andrographis paniculata typically grows to a height of 30-110 centimeters, with a slender and erect stem. The stem is quadrangular in shape, featuring distinct longitudinal ridges and greenish-brown in color. The plant exhibits a bushy growth habit, with numerous branches emerging from the main stem. The leaves are simple, opposite in arrangement, and exude a distinct bitter taste when chewed.
The leaves of Andrographis paniculata are lanceolate in shape, measuring approximately 5-10 centimeters in length and 1-3 centimeters in width. They possess a smooth texture and a glossy dark green coloration, which adds to the plant’s aesthetic appeal. The leaf margins are serrated with small teeth, further enhancing their distinctive appearance.
The inflorescence of Andrographis paniculata consists of small, tubular flowers arranged in compact, axillary clusters. The flowers have a unique and striking appearance, with their corollas divided into two lips. The upper lip is hooded and contains two lobes, while the lower lip is three-lobed. The color of the flowers varies from pale lilac to white, often with purple markings.
Following successful pollination, the flowers of Andrographis paniculata give rise to small, oblong capsules. These capsules are initially green and fleshy, but as they mature, they turn brown and become dry. Each capsule contains numerous tiny seeds, which are released upon the capsule’s splitting, allowing for dispersal by wind or other means.
Andrographis paniculata thrives in warm and humid environments, preferring well-drained soils with a slightly acidic to neutral pH range. It is typically propagated through seeds, which germinate within a few weeks under optimal conditions. The plant requires moderate watering and benefits from partial shade to full sun exposure.
Historical Aspects
Andrographis paniculata holds a rich history of traditional use spanning several centuries. Indigenous to South Asia, including India, China, and Thailand, this herbaceous plant has been revered for its medicinal properties and played a significant role in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Ancient Ayurvedic texts, dating back thousands of years, mention Andrographis paniculata as a potent herb for promoting overall health and treating various ailments. In Ayurveda, it is known by the Sanskrit name “Kalmegh,” which translates to “dark cloud,” possibly referring to its dark green leaves and bitter taste. In traditional Ayurvedic medicine, the plant is primarily associated with its ability to support the immune system and promote digestion.
Similarly, Andrographis paniculata has been a prominent herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), where it is referred to as “Chuan Xin Lian.” It is highly regarded for its bitter properties and is believed to have a cooling effect on the body. In TCM, the plant is traditionally used to clear heat, resolve toxins, and treat conditions such as respiratory infections, digestive disorders, and fevers.
Historically, Andrographis paniculata has been utilized to address a wide range of health concerns. It has been employed as a natural remedy for fever, common cold, cough, bronchitis, and upper respiratory tract infections. The herb’s anti-inflammatory properties have also made it a preferred choice for conditions related to inflammation, such as arthritis and various skin disorders.
The historical use of Andrographis paniculata is not limited to its medicinal applications. In some regions, the plant has been employed for culinary purposes, adding a bitter flavor to certain dishes and beverages. Additionally, the plant has found use in traditional rituals and ceremonies, symbolizing purification and protection.
Bioactive Substances
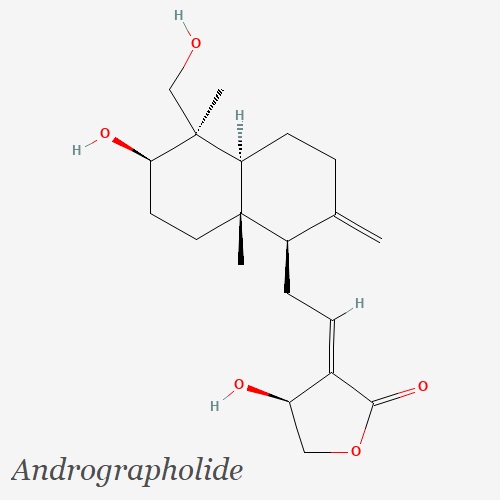
Andrographis paniculata contains several bioactive substances. These chemical compounds, found in various parts of the plant, contribute to its medicinal properties and have garnered considerable attention in scientific research. The bioactive substances of Andrographis paniculata encompass a diverse range of compounds, including andrographolides, flavonoids, diterpenoids, and other secondary metabolites.
Andrographolides are one of the primary bioactive constituents found in Andrographis paniculata. They belong to the class of labdane diterpenoids and are considered the most pharmacologically active components of the plant. These compounds, including andrographolide, dehydroandrographolide, and neoandrographolide, possess various therapeutic properties such as anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and hepatoprotective activities. Andrographolides are known to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, modulate immune responses, and exhibit antioxidant effects, making them valuable in the treatment of inflammatory and immune-related disorders.
Flavonoids are another prominent group of bioactive compounds found in Andrographis paniculata. These polyphenolic compounds, such as apigenin, luteolin, and kaempferol, contribute to the plant’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Flavonoids have been shown to scavenge free radicals, inhibit inflammatory enzymes, and modulate immune responses. Their presence in Andrographis paniculata supports the plant’s traditional use in conditions related to oxidative stress, inflammation, and immune system dysregulation.
Diterpenoids, including andrographiside, 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide, and 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide succinic acid monoester, are bioactive compounds with diverse pharmacological activities. These compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antiviral, and antimalarial properties. They have demonstrated potential in the management of liver disorders, viral infections, and malaria.
In addition to the major bioactive constituents, Andrographis paniculata contains other secondary metabolites that contribute to its medicinal properties. These include xanthones, such as andropanoxanthin and 3-deoxy-3,19-didehydroandrographolide, which possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Alkaloids, such as andrographine and andrographidine, have also been identified in the plant, although their pharmacological significance requires further exploration.
The bioactive substances of Andrographis paniculata are typically extracted from the aerial parts of the plant, particularly the leaves and stems. Extracts derived from these plant parts are used in various forms, including capsules, tablets, tinctures, and topical preparations, to harness the therapeutic potential of the bioactive compounds.
The identification and isolation of these bioactive substances have fueled the growing interest in Andrographis paniculata as a valuable source of natural products for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. Extensive scientific research continues to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of action and explore the potential therapeutic applications of these bioactive substances, contributing to the expanding knowledge base surrounding Andrographis paniculata and its medicinal properties.
Potential Health Benefits
The extracts derived from this plant, as well as its bioactive substances, have been the subject of scientific investigation to explore their potential health benefits. While further research is warranted, preliminary studies suggest that Andrographis paniculata extracts and its bioactive compounds may be useful in addressing several health conditions. The following is a detailed description of some of these potential benefits:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Andrographis paniculata extracts and its bioactive constituents, particularly andrographolides, have shown significant anti-inflammatory effects in both in vitro and in vivo studies. They have been found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulate inflammatory pathways. These properties indicate potential applications in the management of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and allergic reactions.
- Immune System Modulation: Andrographis paniculata extracts have been reported to possess immunomodulatory effects. They have shown the ability to enhance immune responses by stimulating the production of immune cells and cytokines, thereby supporting the body’s defense mechanisms. These properties suggest potential applications in boosting the immune system and improving resistance against infections.
- Antiviral Activity: Studies have demonstrated that Andrographis paniculata extracts and its bioactive compounds exhibit inhibitory effects against various viruses, including influenza viruses, herpes simplex virus, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These findings suggest their potential utility in the prevention and treatment of viral infections.
- Antioxidant Effects: The bioactive substances present in Andrographis paniculata possess antioxidant properties, helping to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. These effects indicate potential benefits in combating oxidative damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and supporting overall cellular health.
- Hepatoprotective Effects: Andrographis paniculata extracts have been studied for their hepatoprotective properties, showing the ability to protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins, drugs, and oxidative stress. These findings suggest potential applications in liver health and the management of liver disorders.
- Digestive Health: Traditional use of Andrographis paniculata in digestive disorders aligns with preliminary scientific evidence. The extracts have been found to possess gastroprotective effects and may help alleviate symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders such as gastritis and gastric ulcers.
- Anti-cancer Potential: Some studies have explored the anticancer potential of Andrographis paniculata extracts and its bioactive compounds. They have shown promising effects in inhibiting the growth and inducing apoptosis (cell death) in various cancer cell lines. However, further research is needed to understand their mechanisms of action and potential applications in cancer treatment.
Conclusions
In both ancient and modern medicine, Andrographis paniculata, or its bioactive substances, has held significant importance. The historical use of this plant in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine highlights its enduring reputation as a medicinal herb. The bioactive substances found in Andrographis paniculata, including andrographolides, flavonoids, and diterpenoids, have been extensively studied for their therapeutic properties. From its traditional applications in addressing fevers, respiratory infections, and digestive disorders, to its potential modern applications in inflammation, immune modulation, antiviral activity, and hepatoprotection, Andrographis paniculata continues to be a subject of scientific exploration. While further research is necessary to fully understand its mechanisms of action and establish its clinical efficacy, the historical and modern usage of Andrographis paniculata underscores its significance as a valuable botanical resource with potential applications in integrative medicine and pharmaceutical development.