
The onion (Allium cepa L.) is a member of the Liliaceae family, which also includes garlic (Allium sativum L.). These two plants share many properties and health benefits. There are many types of onions: the long onion, the round onion, the red onion, the white onion, and so on. They all have a similar, characteristic flavor.
The Latins called the onion caepa. Dioscorides, a Greek physician and pharmacologist, wrote in his text “De Materia Medica” that onion was a useful medicinal plant with properties such as diuretic, antiseptic, and expectorant. He also described onion as a remedy for a number of ailments such as digestive disorders, respiratory problems and wounds.
Onions have a long history of use in traditional medicine and have been used as a folk remedy for various ailments for thousands of years.
In traditional Chinese medicine, onions are believed to have several health benefits. They were believed to have warming properties and help improve circulation, boost the immune system, remove toxins, and relieve symptoms such as coughs and sore throats. They are also believed to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
In India, onions are highly valued for their medicinal properties. They were used in Ayurvedic medicine for their antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, and as a remedy for digestive and respiratory problems. Onions are considered to have warming and pungent qualities and are believed to help stimulate digestion, boost immunity, and clear respiratory infections. They are also used to relieve symptoms of coughs, colds and fevers. In Ayurvedic practice, onions may be used in various forms such as raw, cooked, or in combination with other herbs and spices.
Onions have a long history of use in traditional European medicine, particularly in the folklore of rural communities. They were commonly used to treat a variety of ailments such as coughs, colds, and respiratory infections. Onions were also used as a tonic to strengthen the immune system and improve circulation. In some cases, they were even applied topically to treat wounds and skin conditions. While these traditional uses of onions have not been extensively studied, some scientific evidence suggests that they may have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Onions contain a variety of biologically active compounds that contribute to their health benefits, including:
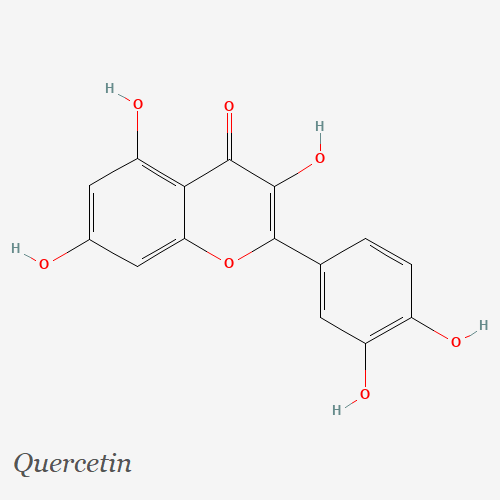
1. Quercetin is a flavonoid found in fruits, vegetables, and grains that is often sold as a dietary supplement. It is marketed as a dietary supplement because of its potential health benefits, including:
- Antioxidant: Its antioxidant properties help protect cells from damage caused by harmful molecules known as free radicals.
- Anti-inflammatory: Quercetin may help reduce inflammation, which is thought to play a role in the development of a number of chronic diseases.
- Cardiovascular health: Quercetin may help improve cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and improving blood flow.
- Allergy relief: Quercetin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effects, which may make it useful in the treatment of allergies.
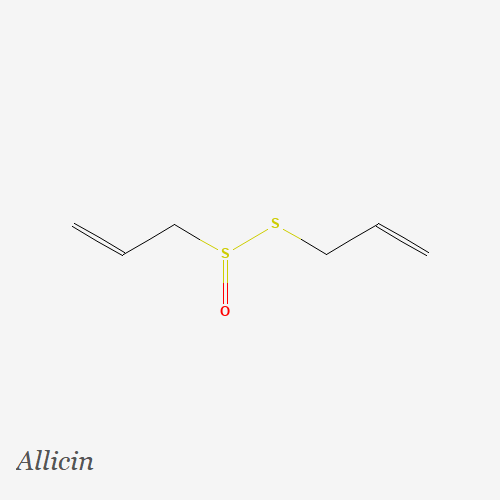
2. Allicin is an organosulfur compound whose potential health benefits include:
- Antimicrobial: Allicin has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, meaning it may be effective against harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Anti-inflammatory: The anti-inflammatory effects of allicin may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
- Cardiovascular health: Allicin may help improve cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Immune system support: Allicin has immune-boosting properties that may help protect against infections and other diseases.
3. Vitamin C: Onions are a good source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that helps boost the immune system and protect against cell damage.
4. Folate: Onions are a good source of folate, a B vitamin that is important for cell growth and development.
It is important to note that the biological activities of the compounds found in onions are complex and depend on the specific compound and dose. In addition, these compounds may interact synergistically with each other. For example, one study found that the maximum plasma concentration of quercetin obtained from powdered onion skin extract was approximately 5 times higher than that obtained when taking pure quercetin, indicating that the bioavailability of the natural product is higher than that of the pure chemical substance.